Types of I.C. Engine
I.C. engine is widely used in automobile industries so it is also known as automobile engine. An automobile engine may be classified in many manners. Today I am going to tell you some important classification of an automobile engine.
According to number of stroke:
1. Two stroke engine
In a two stroke engine a piston moves one time up and down inside the cylinder and complete one crankshaft revolution during single time of fuel burn. This type of engine has high torque compare to four stroke engine. These are generally used in scooters, pumping sets etc.
2. Four stroke engine
In a four stroke engine piston moves two times up and down inside the cylinder and complete two crankshaft revolutions during single time of fuel burn. This type of engines has high average compare to two stroke engine. These are generally used in bikes, cars, truck etc.
According to design of engine:
1. Reciprocating engine (piston engine)
In reciprocating engine the pressure force generate by combustion of fuel exerted on the piston (A device which free to move in reciprocation inside the cylinder). So the piston starts reciprocating motion (too and fro motion). This reciprocating motion converts into rotary motion by use of crank shaft. So the crank shaft starts to rotate and rotate the wheels of vehicle. These are generally used in all automobile.
2. Rotary engine (Wankel engine)
In rotary engine there is a rotor which frees to rotate. The pressure force generate by burning of fuel is exerted on this rotor so the rotor rotate and starts to rotate the wheels of vehicle. This engine is developed by Wankel in 1957. This engine is not used in automobile in present days.
According to fuel used:
1. Diesel engine
These engines use diesel as the fuel. These are used in trucks, buses, cars etc.
2. Petrol engine
These engines use petrol as the fuel. These are used in bikes, sport cars, luxury cars etc.
3. Gas engine
These engines use CNG and LPG as the fuel. These are used in some light motor vehicles.
4. Electric engine
It is eco-friendly engine. It doesn’t use any fuel to burn. It uses electric energy to rotate wheel.
According to method of ignition:
1. Compression ignition engine
In these types of engines, there is no extra equipment to burn the fuel. In these engines burning of fuel starts due to temperature rise during compression of air. So it is known as compression ignition engine.
2. Spark ignition engine
In these types of engines, ignition of fuel start by the spark, generate inside the cylinder by some extra equipment. So it is known as spark ignition engine.
According to number of cylinder:
1. Single cylinder engine
In this type of engines have only one cylinder and one piston connected to the crank shaft.
2. Multi-cylinder engine
In this type of engines have more than one cylinder and piston connected to the crank shaft.
According to arrangement of cylinder:
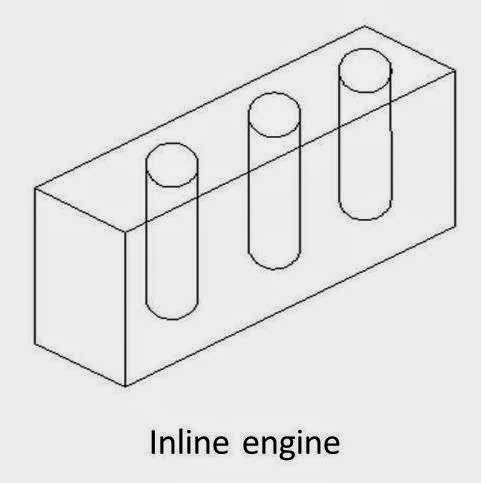
1. In-line engine
In this type of engines, cylinders are positioned in a straight line one behind the other along the length of the crankshaft.
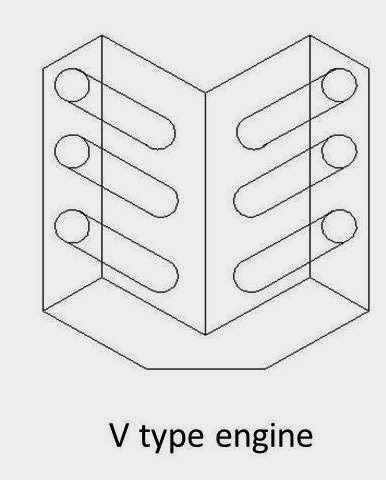
2. V-type engine
An engine with two cylinder banks inclined at an angle to each other and with one crankshaft known as V-type engine.
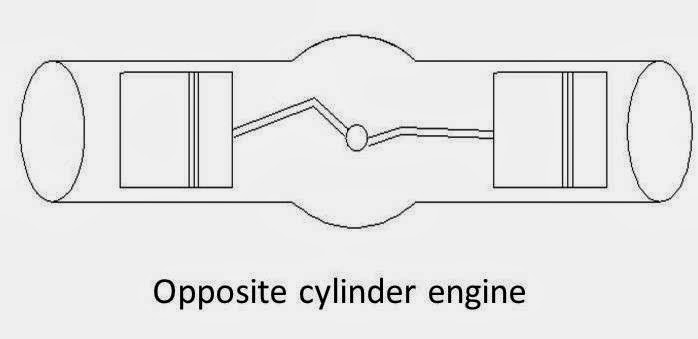
3. Opposed cylinder engine
An engine with two cylinders banks opposite to each other on a single crankshaft (V-type engine with 180o angle between banks).
4. W-type engine
An engine same as V-type engine except with three banks of cylinders on the same crankshaft known as W-type engine.
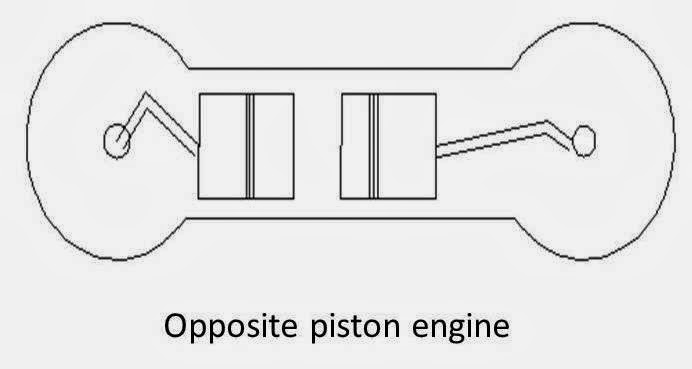
5. Opposite piston engine
In this type of engine there are two pistons in each cylinder with the combustion chamber in the center between the pistons. In this engine a single combustion process causes two power strokes, at the same time.
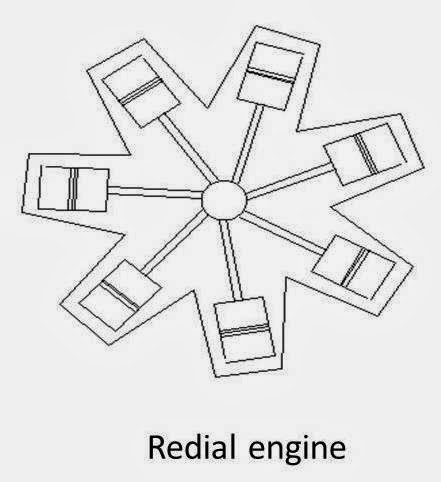
6. Radial engine
It is an engine with pistons positioned in circular plane around the central crankshaft. The connecting rods of pistons are connected to a master rod which, in turn, connected to the crankshaft.
ref: http://www.mech4study.com/